Metal-oxide nanocrystals doped with aliovalent atoms can exhibit tunable infrared localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPRs). Yet, the range of dopant types and concentrations remains limited for many metal-oxide hosts, largely because of the difficulty in establishing reaction kinetics that favors dopant incorporation by using the co-thermolysis method.
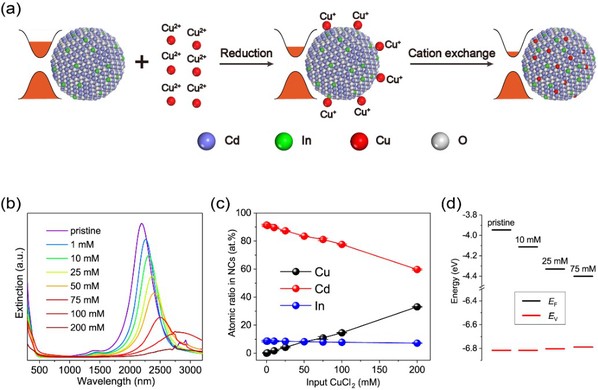
Recently, Prof. Wanli Ma from FUNSOM, Prof. Xingchen Ye from Indiana University developed cation-exchange reactions to introduce p-type dopants (Cu+, Ag+, etc.) into n type metal-oxide nanocrystals, producing programmable LSPR redshifts due to dopant compensation. Cation-exchange transformations add a new dimension to the design of plasmonic nanocrystals, allowing preformed nanocrystals to be used as templates to create compositionally diverse nanocrystals with well-defined LSPR characteristics. The ability to tailor the doping profile postsynthetically opens the door to a multitude of opportunities to deepen our understanding of the relationship between local structure and LSPR properties. Their work has been published in Nature Communications (Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1394), titled as “Tuning infrared plasmon resonances in doped metal-oxide nanocrystals through cation-exchange reactions”.
Link to Paper:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-09165-2#Sec20
Link to Prof. Ma’ group:http://funsom.suda.edu.cn/7f/97/c2735a32663/page.htm
Link to Prof. Ye’ group:https://www.indiana.edu/~yegroup/
Editor:Wenchang Zhu